What is the Crypto Arbitrage Process?
The crypto arbitrage process refers to a trading strategy where investors exploit price discrepancies for the same cryptocurrency across multiple exchanges. This technique takes advantage of the fragmented nature of the digital asset market, where Bitcoin, Ethereum, and altcoins often trade at slightly different prices depending on liquidity, region, and demand.
In theory, the process sounds simple: buy low on one platform and sell high on another. In practice, however, crypto arbitrage is a fast-moving, competitive, and risk-laden strategy that requires deep analysis, speed, and sophisticated tools.
The Mechanics of Crypto Arbitrage
How Price Discrepancies Arise
Unlike traditional stock markets, cryptocurrencies do not have a single centralized exchange. Instead, thousands of platforms worldwide list tokens, each with different order books, liquidity pools, and trading volumes. For instance, Bitcoin might trade at $50,200 on Binance and $50,450 on Coinbase simultaneously. This gap creates an arbitrage opportunity.
Types of Crypto Arbitrage Strategies
- Spatial Arbitrage
This is the classic approach: buying a cryptocurrency on one exchange and selling it on another. It’s most common in markets with regional restrictions, such as exchanges serving only certain countries. - Triangular Arbitrage
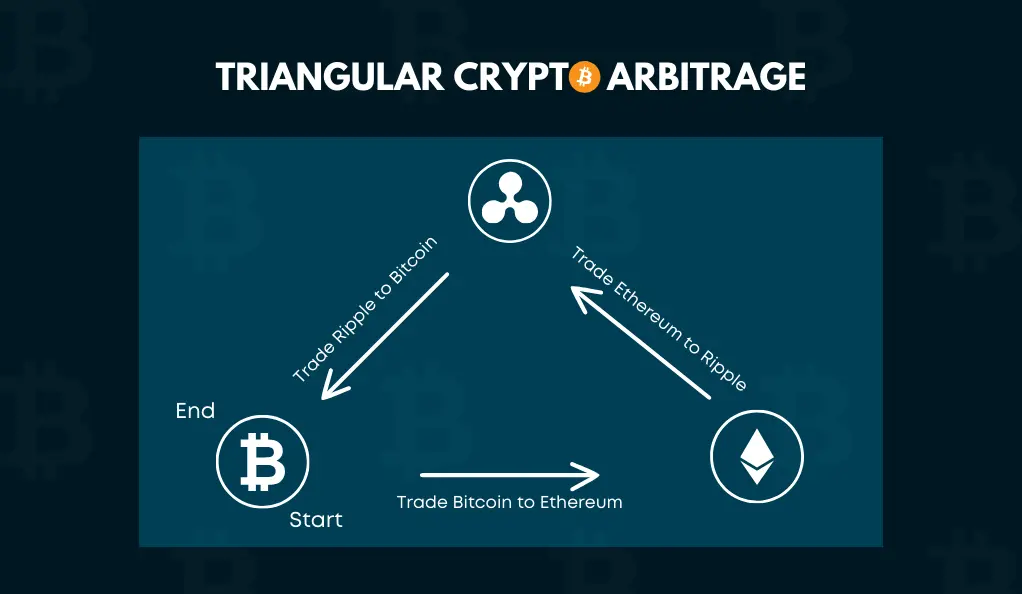
This method involves trading across three different currency pairs within the same exchange. For example, converting BTC → ETH → USDT → BTC to capture price inefficiencies. - Statistical Arbitrage
Traders use algorithms and bots to identify short-term price anomalies across multiple markets. This approach relies heavily on machine learning and automated execution. - Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Arbitrage
With the rise of DeFi, traders can exploit price differences between decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and centralized platforms, or between liquidity pools within protocols like Uniswap and Curve.
The Tools Behind the Process
Executing arbitrage manually is nearly impossible due to how quickly opportunities disappear—sometimes within seconds. Instead, traders rely on specialized tools:
- Arbitrage bots: Automated software designed to scan multiple exchanges and execute trades instantly.
- API integrations: Direct connections with exchanges for low-latency order execution.
- High-frequency trading algorithms: Programs designed to react faster than human traders.
Risks and Limitations of the Crypto Arbitrage Process
While the potential for profit is enticing, several challenges complicate execution:
- Transaction Fees: Exchange fees, withdrawal costs, and gas fees (especially on Ethereum) can wipe out thin profit margins.
- Slippage: The price might change between the moment you spot an arbitrage opportunity and when the trade executes.
- Transfer Times: Moving assets between exchanges is not always instant, creating exposure to volatility.
- Regulatory Risks: Some countries restrict fund transfers, impacting arbitrage efficiency.
- Competition: As more traders deploy arbitrage bots, the profitability window narrows significantly.
Is Crypto Arbitrage Still Profitable in 2025?
The profitability of arbitrage depends on market inefficiencies. In the early days of Bitcoin, spreads between exchanges were wide, and profits could be substantial. By 2025, however, the market has matured. Arbitrage opportunities still exist, particularly in niche altcoins, DeFi protocols, and emerging markets, but they are often razor-thin and dominated by professional trading firms with advanced infrastructure.
According to Cointelegraph, most retail arbitrageurs face shrinking margins unless they use automated systems. A similar analysis by Investopedia suggests that arbitrage remains relevant, but only when traders carefully factor in costs and risks.
Real-World Examples
- South Korean Kimchi Premium: For years, Bitcoin traded at higher prices in South Korea due to local demand, allowing traders to profit by buying abroad and selling domestically.
- USDT Price Variations: Tether (USDT) often fluctuates slightly above or below $1 depending on the platform, enabling quick arbitrage plays.
- DEX-CEX Mismatches: Liquidity pools in DeFi can temporarily misprice tokens compared to centralized exchanges.
How to Start the Crypto Arbitrage Process
- Research and Setup
Open accounts across multiple exchanges, verify KYC requirements, and connect trading APIs. - Choose a Strategy
Decide whether to pursue spatial, triangular, or DeFi-based arbitrage. - Automate the Process
Use arbitrage bots or trading software for execution. Manual trading is rarely effective. - Test with Small Amounts
Begin with low capital to understand transfer times, fees, and execution risks. - Scale Gradually
Only after mastering the process and covering costs should you scale trading volume.
For a step-by-step beginner’s guide, you can explore Binance Academy.
FAQs: What is the Crypto Arbitrage Process?
Q1: What is the crypto arbitrage process in simple terms?
The crypto arbitrage process is buying cryptocurrency at a lower price on one exchange and selling it at a higher price on another to profit from market inefficiencies.
Q2: How risky is the crypto arbitrage process?
It carries risks such as transaction fees, transfer delays, market volatility, and increased competition from automated bots.
Q3: Can beginners profit from the crypto arbitrage process?
Yes, but beginners must start small, use reliable platforms, and factor in costs. Without automation, opportunities often vanish too quickly.
Q4: Is the crypto arbitrage process legal?
Yes, arbitrage trading is generally legal, though traders must comply with local regulations and tax obligations.
Q5: Will the crypto arbitrage process remain profitable in the future?
Arbitrage will likely remain but with shrinking profit margins. Advanced traders and institutional investors are better positioned to benefit in the long term.
Conclusion: The Future of the Crypto Arbitrage Process
The question “what is the crypto arbitrage process?” goes beyond a simple definition. While the core principle—profiting from price discrepancies—remains timeless, the environment in 2025 is highly competitive and technologically driven. Profitability is still possible, but success now requires automation, cross-market insight, and careful risk management.
Looking ahead, arbitrage may evolve alongside innovations in decentralized finance, AI-driven trading, and tokenized assets. Traders who adapt to these changes will continue to find opportunities, but the days of easy profits are long gone.